What Are Low-E Windows?
Last edited
Author
Andrew Giermak
Solar and Electrification Writer and Editor
Editor
Andrew Blok
Electrification and Solar Writer and Editor
Your windows are more than just a view to the outside — they are part of your home’s envelope. Older or single-pane windows can result in heat loss or heat gain, which means losing money on extra heating and cooling. Old windows can be responsible for up to 30% of a typical home's heating and cooling loss.
Low-E windows solve this by using an invisible coating or film that reflects heat, keeping heat inside during the winter and blocking solar heat in the summer. If you’re looking to cut utility bills without sacrificing natural light, understanding Low-E technology is a step toward a more comfortable, cost-effective home.
See how much you can save with home energy changes
What are Low-E windows?
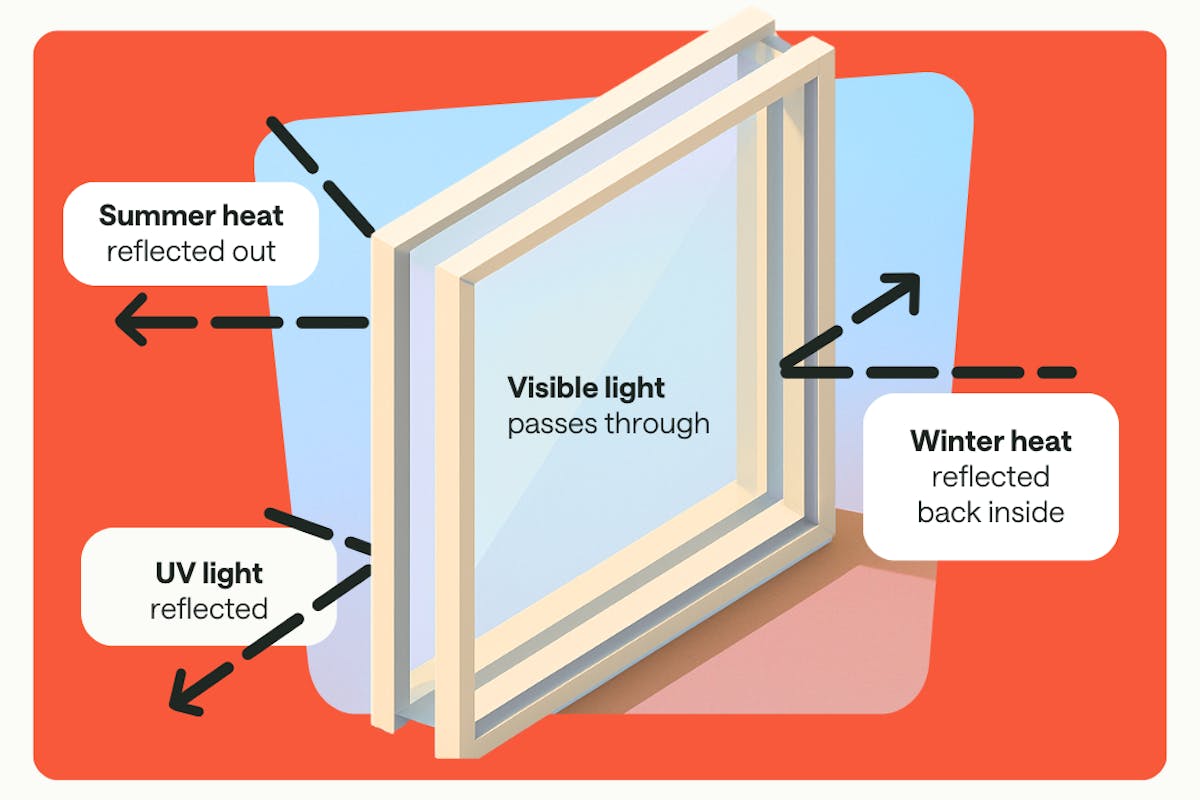
Low-E is short for low emissivity. Heat naturally wants to move from a warmer area to a cooler area. When it’s cold outside, it’s warmer in your house and heat will escape through a window. When it’s hot out, the heat outside will naturally radiate or pass through a window into your home.
A low-E window is a double- or triple-pane window and has a thin coating you can’t see, unless it is tinted, on one pane that slows the passage of heat in both directions, so it saves you energy and money year-round.
What are the benefits of Low-E windows?
The primary benefits with low-E windows are better energy efficiency and savings for your home heating and cooling. More heat stays in your home in winter and more heat stays out in summer. Here are other positives to consider.
- Lower energy bills: Low-E windows let your HVAC system run less whether it’s heating or cooling. A range of commercial sites give a range of estimated annual savings of $27-$500. Savings depend on factors such as climate, energy rates, number of windows replaced, and the condition of the old windows (you’re likely to save more if you’re replacing older or single-pane windows).
- UV radiation protection: The low-E glass coating blocks most UV radiation which stops ambient heat as well as wear and damage to floors and furniture.
- Natural light: While there are tinted options, non-tinted low-E windows give you the benefits of energy efficiency while still letting natural light in so you have the health benefits, aesthetics, and further energy savings of letting sunlight into your home.
Does Low-E window film or tint work?
There are window film and window tint products which can give you some of the same benefits as low-E windows while being more budget-friendly.
Low-E film goes on the interior of a window pane and is primarily used to keep heat in or out and keep UV rays out. Drawbacks of using film are the product won’t have the likely lifespan or durability of new windows, or the air sealing effect of new windows, so heat/energy may still be lost in drafts or older windows or frames. Adding film may void a warranty if you have one on your windows.
Low-E tint decreases the solar energy and visible light passing through a window. So, in summer, tint reduces heat gain inside. Using only tint, but no low-E pane or film, makes a much smaller difference in heat loss during cooler weather and seasons.
See how much you can save with home energy changes
Windows and energy efficiency
Installing new low-E windows or using film or tint to control heat loss or gain are good steps to greater energy efficiency and comfort in your home. There are other tips and projects you can do to make your windows part of saving energy and saving money year around.
Data from the US Department of Energy shows 25-30% of heat gain or loss in an average house happens through the windows.
Shy of replacing your home’s windows, energy-saving tasks can include checking and adding caulk and weatherstripping along windows. Adding or remembering to use curtains or blinds can create shade and an extra layer of insulation when needed. Even outside around your windows and home, using awnings or planting trees and shrubs to create natural shade and windbreaks can moderate temperatures and take some of the load off your heating and cooling system. A home energy audit can check insulation levels, window sealing, and temperature differences between rooms or floors, or near windows and doors, to show you more ways to save.
If you’re looking at more ways to save energy or move toward home electrification, get actionable ideas and customized estimates with Palmetto’s Savings Maximizer.
See what home electrification can do for you:
Frequently asked questions
What are low-E windows?
Low-E windows have coated window panes to keep heat inside when it’s warmer inside than out, and heat outside when it’s warmer outside than in. Low-E windows may be an energy-efficient addition to your home plus give you more comfortable and consistent temperatures.
Is low-E window film worth it?
Low-E window film insulation can give you some of the same temperature control and energy efficiency as low-E window panes, but without the larger expense of new windows. They are generally not as effective as low-E windows.
How do windows affect a home’s energy efficiency?
Windows and window frames can be a major point of heat loss or gain in a home and heating and cooling is a major source of energy usage in most homes. Old, poorly-sealed, or single-pane windows can be drafty, leaky, and allow energy loss you wind up paying for.


