How Solar Energy Works: Step by Step
Last edited
Author
Andrew Blok
Electrification and Solar Writer and Editor
Editor
Ryan Barnett
SVP, Policy & New Market Development
The sun gives us more energy than we could possibly use. It’s clean, free, renewable, and effectively infinite power. Turning that solar energy into clean electricity we can use in our homes, businesses, vehicles, and technology is happening now and creating a more abundant future today. Abundant renewable energy from solar panels can help keep energy prices down, cut your power bill, and leave the air and environment cleaner.
But how does solar power work? How do solar panels pull off this magic trick? If you have home solar panels, here's how they turn sunlight into the electricity you use everyday.
See how much you can save by going solar with Palmetto
What is solar energy?
Solar energy is the solar radiation emitted from the sun. Earth receives enough of that renewable energy on a daily basis to cover every user of electricity on the planet. That’s one powerful energy source!
How does solar energy produce electricity? People have come up with several ways to capture solar energy, the most common being photovoltaic (PV) solar panels that convert the sun's rays into electricity. Solar panels aren’t making or creating the energy, they are just converting it from sunlight to electricity.
With that information in mind, here's how solar energy works step by step.
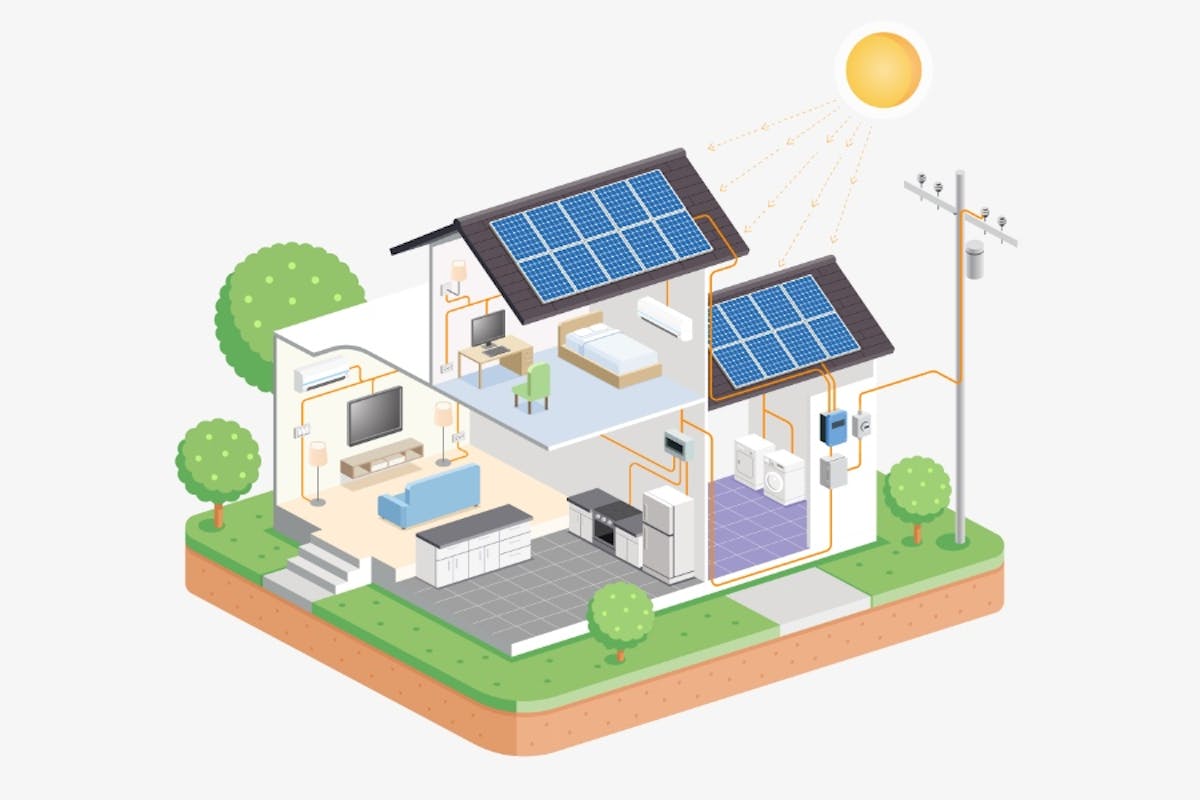
Step 1: Solar panels capture solar energy
Solar panels convert solar energy from sunlight into electrical energy. The most common solar panels are made from one of three semiconductors: monocrystalline silicon, polycrystalline silicon, or thin-film solar cells.
When sunlight hits the thin layer of semiconductive material, it triggers the release of electrons from silicon atoms. The negatively-charged electrons are attracted to the positively-charged side of the cell. This photovoltaic effect results in free-flowing electrons within the solar panel. The moving electrons create an electric current which is harnessed by the wiring connected to the solar panels to produce electricity.
Solar power systems are carbon-free in their energy production. The lifetime emissions of solar panels, which includes emissions from the manufacturing of panels, is about 12 times less than lifetime emissions from a natural gas plant and about 20 times less than from a coal plant.
The more sunlight that reaches the solar panels, the more energy they generate, which means they generate more or less electricity depending on the season.
A solar installation company should walk you through and help you understand factors ranging from specifics about your property, such as shading and your family’s typical power usage, to your climate and geographical location.
Solar panels can be tilted to capture the most sunlight at the optimal angle for the best efficiency. Usually, that angle matches your latitude. In the lower 48, that spans from 24.5 degrees in Key West, Florida to 49.2 degrees in Angle Inlet, Minnesota.
See how much you can save by going solar with Palmetto
Step 2: Solar inverters convert DC to AC
Solar panels produce electricity in the form of direct current (DC), which means the electricity flows in only one direction. However, your home appliances use alternating current (AC) electricity, which means the electricity flows in both directions.
This means the solar electricity from your panels needs to be converted from DC to AC to make it usable in your home. To convert DC power to AC power, you need an inverter.
It’s a simple job, but an essential one. Without the inverter, your system would create electricity, but it wouldn’t be able to power anything, except maybe charging batteries.
The type of inverter you use depends upon the size and configuration of your home solar energy system. A simpler system typically uses a string inverter, a single box in a central location near your circuit breaker. More intricate systems use microinverters in which each panel has its own individual inverter. Other inverter options include power optimizers and hybrid inverters, depending upon your home’s energy needs.

Credit: National Renewable Energy Laboratory
Solar inverters also allow you to connect your solar panel system to the internet so you can access information about your system’s performance. This helps you compare your solar energy production and your household energy consumption so you can check if the system is functioning properly and meeting your electrical load as required.
The Palmetto app offers an easy way to stay on top of how much electricity your solar panels are generating and how much electricity you're buying from the grid. Even better, when you take action to save energy, you can earn discounts on energy saving upgrades, like smart thermostats and EV chargers.
Step 3: Electrical panel distributes electricity
Your electrical panel distributes electricity throughout your home, whether that’s your dishwasher, refrigerator, or energy-efficient heat pump. The circuit breakers in the electrical panel can also cut the current to an electrical circuit in case a fault or surge occurs, to prevent an overload in electrical lines that can cause damage.
Lastly, electrical panels are also a key component of consumption monitoring. There are devices that can be attached to either the main panel or each individual circuit, allowing you to view more details about your specific energy consumption, which can help you optimize your energy usage over time. A smart electrical panel can act as the brain that optimizes how your home uses electricity and the eyes that keep tabs on electricity use, too.
See how much you can save by going solar with Palmetto
Step 4: Electric meter records consumption and production
Your electric meter (sometimes called the “utility meter”) is the device your utility company uses to measure your electricity consumption. It’s how it knows what to bill you each month. A traditional electric meter has analog dials that spin as current flows through it, which is why the utility company has someone check your meter in person once a month. That meter reading is just a summary of your electricity consumption for the month.
When you go solar, you consume electricity from your solar panels, which lowers the amount of electricity you consume from the grid. As a result, your electric meter records a lot less consumption, and you save money by not paying for electricity from the utility company.
Most homes with solar have a smart meter installed, which records the exact consumption of electricity for your house. Smart meters send real-time usage data to your local utility company for billing, customer service, and research purposes. A smart meter eliminates the need for estimated bills by measuring exactly how much electricity is being used.
Smart meters and net metering
If your home has a smart meter, it allows you to take advantage of net metering if it’s available in your area. If your solar panel system is connected to the electricity grid (most are) then net metering allows you to get credits from your local utility company for any surplus electricity generation.
Your smart electric meter will record energy production in addition to consumption, and when you generate more energy than you need for your home, you can export that power to the grid and earn credits to reduce future electric bills.

Step 5: Batteries store excess energy
Installing solar battery storage can unlock greater long-term benefits of going solar. If your solar panels generate more solar energy than you can use, you can store that extra electricity in a solar battery. That way, you have electricity available to you when the sun goes down or it’s a rainy day — instead of drawing from the electricity grid.
Depending on the type, solar batteries can either store excess DC electricity that’s produced by your solar panels, or they can be charged by AC electricity that’s already been converted by your inverter.
Many states and power companies now have incentives for residential customers who send excess power from their solar batteries to the overall electric grid. These programs, called virtual power plants, help spread out when renewable energy can be used on the grid. At times of surplus solar, wind, or other renewable energy production, the excess is stored. When it’s later added to the grid, those sharing their battery’s power with the grid are compensated.
Solar battery storage is growing and is expected to continue growing exponentially. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory estimates energy storage will multiply by at least five times from 2020 to 2050.

Source: National Renewable Energy Laboratory
Will solar energy work for your home?
Solar energy at home can deliver real benefits. You can lower your utility bills, reduce your carbon footprint, increase your independence from the electricity grid, help create a clean energy future, and more.
Solar energy is also the fastest growing and (by some counts) cheapest source of energy today. If you're interested in whether or not solar will work at your home, get a free solar savings estimate today, or download the Palmetto app to see how else you can save energy and money at home.
See what solar can do for you:
Frequently asked questions
How do solar panels work?
Solar panels convert solar radiation into electricity, then an inverter turns it into the AC electricity that’s usable in your home. Sunlight hits semiconductive material on a panel and creates a flow of electrons. This electric current moves through wiring on the panel to your home.
Are solar panels good for the environment?
Yes, solar energy is a completely renewable source of power. Solar systems produce no emissions via their energy production, and they for decades with very good efficiency.
Can solar panels save money?
Yes, solar panels can save money. In many — but not all — cases, solar panels can save you as much as they cost in 6-10 years. This period of time is also known as a solar payback period.


